One Primitive Trait of Ardipithecus Ramidus Is Its
Scientists have been studying one particular Ardipithecus ramidus skeleton almost complete for 17 years and today they released their findings. Ardipithecus kadabba was bipedal walked upright probably similar in body and brain size to a modern chimpanzee and had canines that resemble those in later hominins but that still project beyond the tooth row.

Did Ardipithecus Ramidus Roam The Woods Or The Grasslands Csmonitor Com
The basal Gaala Tuff Complex GATC and the Daam Aatu Basaltic Tuff DABT.
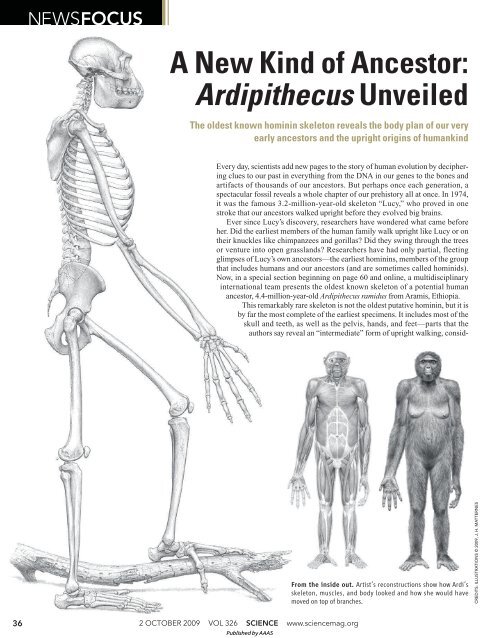
. Ardipithecus ramidus is a species of australopithecine from the Afar region of Early Pliocene Ethiopia 44 million years ago mya. Primitive characteristics of ardipiths can be seen in many body regions. Ramidus was named in September 1994.
One primitive trait of Ardipithecus ramidus is its Group of answer choices pelvis. Fossils have also been found in Kenya which could belong to specimens of Ardipithecus ramidus. However it would not have been as efficient at bipedality as humans nor at arboreality as non.
One primitive trait of Ardipithecus ramidus is its O pelvis. Ramidus preserves many primitive ancestral characteristics of the last common ancestor with two notable exceptions - ability to walk upright and the absence of the large projecting canine teeth that signify social organization with competition and aggression between males. View the full answer.
100 2 ratings Answer. Instead its teeth were adapted to eating food found in both trees and on land 4. In 2009 scientists announced a partial skeleton nicknamed Ardi.
This early human species is only known in the fossil record by a few post-cranial bones and sets of teeth. However scientists claim that other features of its skeleton reflect adaptation to bipedalism. Biology questions and answers.
Ramidus shares with modern human and Au. Anterior inferior iliac spine indicated by yellow arrow and greater sciatic notch indicated by. Depending on the source their cranial base the inferior portion of the occipital bone was either flat like chimps and gorillas or angled and tucked under the upper part of the cranium termed flexed cranial base or basicranial flexion.
Sexual dimorphism in primates can be indicated by ____ size. Ramidus ate an omnivorous diet without the focus on ripe fruits seen in chimpanzees. Afarensis that are related to bipedality.
One primitive trait of Ardipithecus ramidus is its Ch9. Mutations and Hardy-Weinberg processes. Many of the foots primary adaptations to fulcrumation are probable retentions from the gorillachimpanzeehuman last common ancestor GLCA but.
Ardipithecus ramidus was first reported in 1994. The development of a more modern skull that would allow the expansion of the brain in later hominids and the use or lack of use the arms for locomotion. Ardipithecus ramidus Paleomagnetic uses periodic reversals in the Earths magnetic field.
1 anthropoid foot proportions represented in Ardipithecus are consistent with adaptive optima associated with generally-accepted functional types 2 Ardipithecus shares a number of traits that together. The foot bones in this skeleton indicate a divergent large toe combined with a rigid foot its still unclear what this means concerning bipedal behavior. There it appears that Ar.
Like most primitive but unlike all previously recognized hominins Ardipithecus ramidus had a grasping big toe adapted for locomotion in trees. Ramidus which was discovered in the middle Awash valley in 1992 at a site named Aramis is known from a crushed and distorted partial skeleton. Radioisotopic utilizes the known rate of decay of one radioisotope into another Importantly Ar.
To understand the anatomy of the Ardipithecus ramidus it is necessary to examine Ardi the best preserved specimen of this genusIts remains are key to knowing the details of the teeth pelvis skull and leg of a Ardipithecus female. This is a distinctive feature of the. Ramidus teeth was a lack of premolar complexes or essentially the fangs seen in gorillas and chimpanzees.
The ____ hypothesis states that long term environmental unpredictability led to morphological and behavioral adaptations. Previous question Next question. By 3 million years ago Australopithecines were relatively common in East and South Africa.
2 2009 everything changed. 2Two evolutionary processes that may produce a cline in a human allele or trait are Group of answer choices gene flow and genetic drift. The first fossil found was dated to 44 million years ago on the basis of its stratigraphic position between two volcanic strata.
Opposable toe Ardipithecus ramidus is a hominin species that lived about 45 million years ago during the early pliocene period. Using the morphometric methods with six variables relating to the foot Prang tests explicit competing hypotheses of the Homo-Pan LCA and demonstrates that. Ramidus unlike modern hominids has adaptations for both walking on two legs bipedality and life in the trees arboreality.
Ramidus represents the oldest species that possesses features unequivocally linked to the hominin lineage. One primitive trait of Ardipithecus ramidus is its apelvis. Their brains were small.
The fossils recovered show that Ardipithecus ramidus was a mosaic of traits retaining its opposable big toe. The skull is apelike with a tiny brain300350 cc 183214 cubic inches which is equivalent to a brain weight. Orrorin tugenensis is the first species that indicates adaptations for Ch9.
Another aspect of Ar. Ardipithecus kadabba and Ar. According to lecture which is the earliest species associated with the use of primitive stone tools.
Sexual selection and natural selection. The pelvis reconstructed from a crushed specimen is said to show. Ramidus foot is an amalgam of retained primitive characters as well as traits specialized for habitual bipedality such as the expanded second metatarsal base that anchored plantarflexion during heel- and toe-off.
Ardipithecus has been known about since 1992 but as recently as Spring 2009 I was unable to find information on cranial capacity and or bipedalism. The name Ardipithecus ramidus stems mostly from the Afar language in which Ardi means groundfloor and ramid means root.

Pdf Ardipithecus Ramidus And The Birth Of Humanity
Bbc News Science Environment Fossil Finds Extend Human Story

Probable Behavioral Physiological Character States In Ardipithecus Download Table

Oldest Skeleton Of Human Ancestor Found

Representative Examples Of The Aramis Ardipithecus Ramidus Dentition Download Scientific Diagram

Ardipithecus Ramidus Four Feet To Two Naturally Inspiring

Ardi Human Origins Last Common Ancestor Evolution

Science S Breakthrough Of The Year Uncovering Ardi American Association For The Advancement Of Science

Morphological Character States In Ardipithecus Ramidus Compared With Download Table

8 Ardipithecus Ramidus Ardipithecus Kadabba The History Of Our Tribe Hominini

Solved One Primitive Trait Of Ardipithecus Ramidus Is Its O Chegg Com
The Ethiopian Hominid Ardipithecus Ramidus Astronoo

Cleveland Researchers Say Fossil Find Overturns Thinking On Human Evolution Cleveland Com

Ardipithecus Ramidus One Of The Most Important Anthropological Finds In The Past 20 Years Waiting For More Results On Kadaba Anthropology The Past Key Copy



Comments
Post a Comment